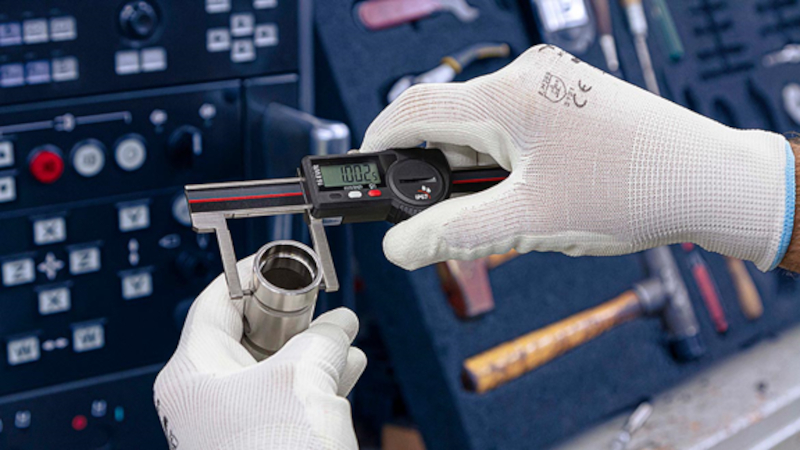
On March 6, the CircleRed project team explored Reverse Engineering during their monthly online meeting.
Reverse engineering (RE) is increasingly employed to address challenges associated with manufacturing spare parts for existing devices when comprehensive technical documentation is unavailable or replacement components are difficult to obtain. The prevalence of such scenarios is projected to rise in the coming years due to the growing emphasis on prolonging device lifespan, driven by environmental considerations and the R3 principle: reduce, reuse, and recycle. [Aladag, Mehmet, et al., Reverse Engineering of Parts with Asymmetrical Properties Using Replacement Materials, Acta Mechanica et Automatica, vol. 16, no. 3, Sciendo, 2022, pp. 250-258. https://doi.org/10.2478/ama-2022-0030]
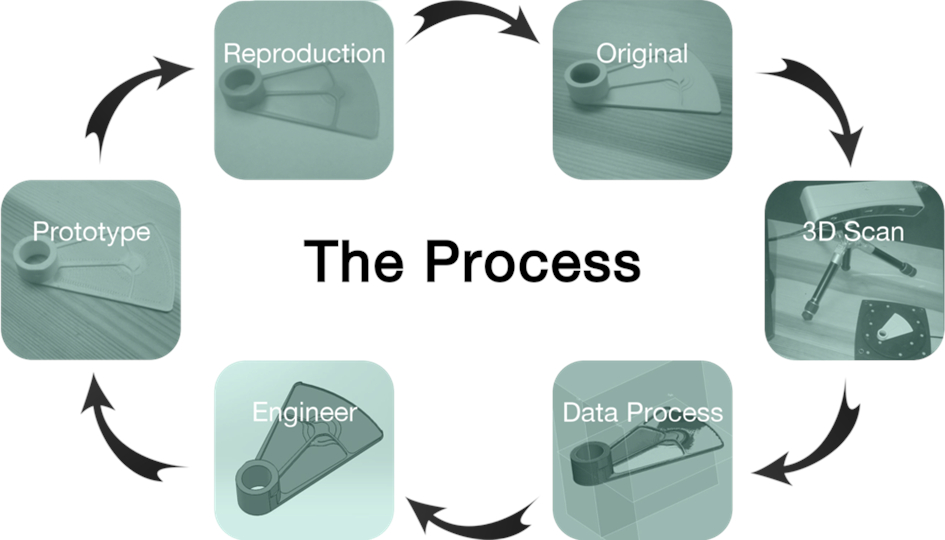
Reverse engineering (RE) is the process of analyzing a subject system to identify the system’s components and their interrelationships and create representations of the system in another form or at a higher level of abstraction.
We can distinguished three main functions of RE:
- To duplicate or produce original equipment manufacturer parts whose design data is not available.
- To repair or replace worn-out parts without knowledge of the original design data.
- To generate a model or prototype based on an existing part for analysis.
RE application areas include:
- software engineering, anti-virus software,
- automotive industry,
- aerospace industry,
- electronics industry,
- enterprise internal transportation, conveyor belts,
- medical industry,
- food industry and 3D food printers,
- sculpting.
Source: Announcing Solid Edge Reverse Engineering Beta | Solid Edge
-
Measuring
-
Photogrammetry
Photogrammetry is a technology that uses a camera or combination of cameras to measure the shape, size, and spatial position of a subject.
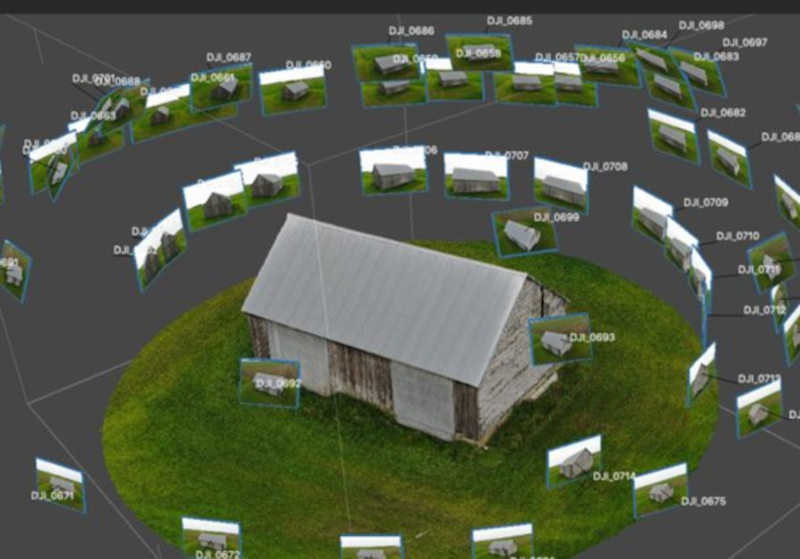

Source: What Is Photogrammetry? Exploring SHINING 3D’s Video Photogrammetry (VPG) -
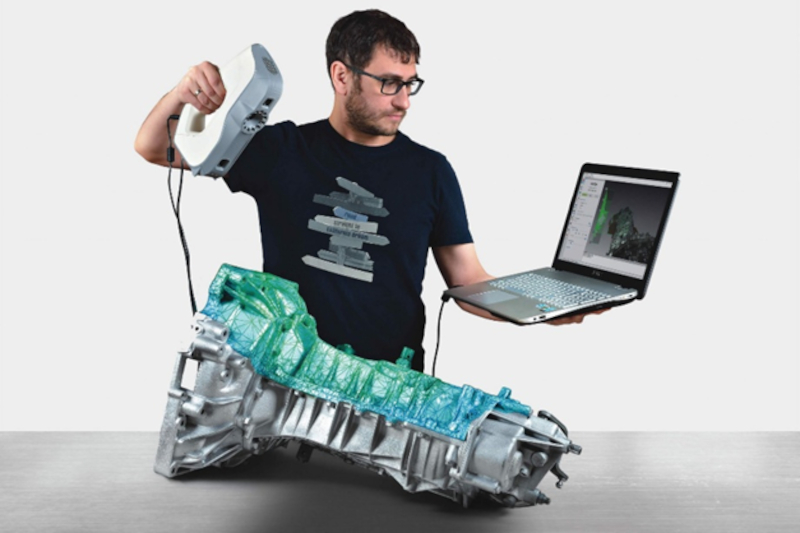
3D Scanning

Source: www.binder3d.com/nieuwsfeed/de-vele-mogelijkheden-van-3d-scanning-en-reverse-engineering
